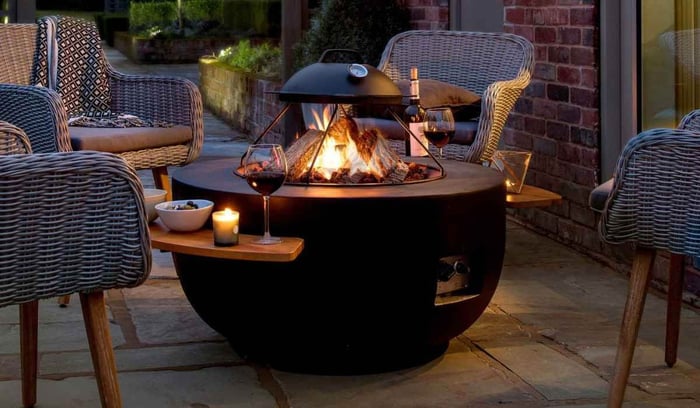
Are you looking to extend your outdoor activities into the colder months but unsure how to keep warm? Gas fire pits might just be your answer, but do gas fire pits keep you warm?
With their enticing flame and contemporary design, gas fire pits have quickly become a favourite feature in gardens and outdoor spaces. These features utilise propane or natural gas to create an inviting, visually appealing fire that can enhance any outdoor gathering.
Despite their undeniable visual charm, one question frequently arises: do they provide sufficient warmth? The answer, in short, is yes; gas fire pits generate a considerable amount of warmth, making them a brilliant source of heat for outdoor settings.
However, the degree of warmth can be influenced by various factors, including the fire pit's BTU (British Thermal Units) rating, prevailing weather conditions, and individual perceptions of warmth.
We will explore these factors in greater detail, comprehensively understanding how gas fire pits produce warmth and helping you make a well-informed choice for your outdoor heating requirements.
Overview of Gas Fire Pits
The concept of gathering around a fire for warmth and camaraderie traces its roots back to ancient times. However, this tradition's modern, convenient incarnation - gas fire pits - is a relatively recent innovation.
As attractive alternatives to wood-burning pits, gas fire pits have become popular for their ease of use, cleanliness, and the captivating ambience they create at the flick of a switch.
Gas fire pits have found their place in various settings, from residential gardens and patios to commercial establishments like restaurants and beer gardens.
They serve as a source of heat and an inviting centrepiece for social interactions, adding a touch of luxury to any outdoor space.
Today, a wide array of gas fire pits is available, each boasting unique features and designs. Here are some of the common types:
Table Fire Pits: These dual-purpose designs incorporate a gas fire pit into a table, providing warmth and a functional piece of furniture.
Fire Bowls: Often portable, these round, bowl-shaped fire pits offer flexibility and can be repositioned to suit your needs.
Fire Pit Tables: Larger than table fire pits, these models produce more substantial heat, making them suitable for larger spaces.
Built-in Fire Pits: Designed as a permanent feature in your outdoor space, these fire pits typically require a natural gas line and offer a seamless aesthetic that can blend with your landscape design.
Each type of gas fire pit delivers a different aesthetic and functional experience, with varying degrees of warmth. The choice of which to install will depend on your individual needs, preferences, and the nature of the space where it will be placed.

How Do Gas Fire Pits Work?
Understanding how gas fire pits work can give you a better appreciation of their efficiency and safety. The basic mechanism behind gas fire pits is fairly straightforward, involving a fuel source, a way to ignite the fuel, and a medium to distribute the flame.
Fuel Source: Gas fire pits primarily use either natural gas or propane as fuel source. Natural gas fire pits require a fixed line, which means they are usually permanently located. On the other hand, propane fire pits use refillable tanks and can be more portable.
Ignition: The ignition method for a gas fire pit varies depending on the model. Some require manual ignition, where you'll need to light the gas as it's released, usually with a long match or lighter. Others have an electronic ignition system, which automatically sparks to ignite the gas once it's released.
Flame Medium: This is the material that the gas flame heats up to create a visually appealing fire effect. It could be artificial logs designed to look like a traditional wood fire, or more commonly, it could be fire glass or lava rocks. These materials don't burn but retain and radiate heat, and the flames that flicker around them create the illusion of a more extensive fire.
When a gas fire pit is turned on, the gas travels from the fuel source through a series of tubes and out through the burner, where it's ignited by the ignition system. The flame medium then heats up and radiates warmth into the surrounding area.
The design and materials used in a gas fire pit can significantly influence its heating capacity and the ambience it creates. Still, the basic principle remains the same: release fuel, ignite it, and distribute the heat efficiently.
Explanation of the Heating Process
The heating process in gas fire pits is an interesting interplay of physics and chemistry. At its core, it's all about combustion - the chemical process where fuel reacts with oxygen to produce heat.
Here's a detailed step-by-step explanation:
Release of Fuel: When you turn on the fire pit, gas (either propane or natural gas) is released from the fuel source and travels through a gas line towards the burner. The amount of gas released can typically be controlled by a valve or dial, allowing you to adjust the size and intensity of the flame.
Ignition: As the gas reaches the burner, it comes into contact with the ignition source. This could be a spark from an electronic ignition system or a flame from a manual lighter or match. The ignition source provides the energy needed to start the combustion process.
Combustion: When the gas is ignited, a chemical reaction takes place. The fuel (in this case, the gas) reacts with oxygen in the air, breaking down the gas molecules and forming new ones. This process releases significant heat - the same principle that heats a gas cooker or boiler.
Heat Distribution: The flames from the combustion process heat the flame medium (such as fire glass or lava rocks) in the pit. These materials absorb heat and then radiate it outward, warming the surrounding area. The heat felt will depend on proximity to the fire pit and external factors, such as wind or outdoor temperature.
The beauty of gas fire pits is their ability to provide instant heat. Unlike wood-burning fires, there's no waiting for logs to catch alight and no tending necessary to keep the fire going. With a gas fire pit, heat is available at the flick of a switch or the turn of a dial.
The Importance of BTUs/kW
When considering any heating system, including gas fire pits, two key measurements are crucial in determining their heating capability: British Thermal Units (BTUs) and kilowatts (kW). These units measure the heat output, and understanding what they represent can help you choose a fire pit that meets your heating needs.
British Thermal Units (BTUs): This is a traditional unit of heat, defined as the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. Regarding heating systems, BTUs indicate the amount of heat the system can produce per hour. The higher the BTUs, the greater the heat output.
Kilowatts (KW): A kilowatt is a unit of power that equals 1,000 watts. In the context of heat output, it is used in many parts of the world, including the UK, instead of BTUs. To convert BTUs to kilowatts, you can divide the BTU rating by approximately 3,412.

Why Are These Measurements Important?
Determining Heat Output: BTU or kW ratings are essentially the 'horsepower' of your gas fire pit. They tell you how powerful the fire pit is, or in other words, how much heat it can generate. This is crucial in determining if a particular fire pit will provide enough heat for your space.
Efficiency Considerations: These measurements can also give you an idea about fuel efficiency. A high BTU or Kw rating fire pit will consume fuel faster. So, you'll need to balance the need for heat output with the fuel cost.
Size and Spacing: The heat output can influence the size of the fire pit you need and how you arrange your outdoor space. Higher BTU or Kw ratings will provide more heat and cover a larger area.
By understanding these measurements, you can make an informed decision when choosing a gas fire pit, ensuring that it can provide the right amount of warmth for your outdoor space.
Can You Control the Heat Output?
One of the primary advantages of gas fire pits over their wood-burning counterparts is the level of control they offer over the heat output. Most gas fire pits are equipped with features that allow users to adjust the flame and, consequently, the heat produced.
Flame Control: Most gas fire pits have a control knob or dial to adjust the burner's flow. By increasing the flow, you generate a larger flame and more heat. Conversely, reducing the gas flow leads to a smaller flame and less heat. This feature allows you to control the ambience and warmth according to your preference and the weather conditions.
Ignition Control: Some high-end models come with an electronic ignition system. With these, you can instantly turn the fire pit on or off, providing another layer of control over the heat output. It also adds a level of safety, as the fire can be extinguished immediately if necessary.
Heat Distribution Media: The choice of heat distribution media, like fire glass or lava rocks, can also influence the perceived heat output. Different materials absorb and radiate heat differently. Some materials may retain and radiate heat more effectively than others, contributing to the overall warmth felt from the fire pit.
The heat output of a gas fire pit is not fixed. With the right features and materials, you can adjust the heat to suit your comfort and the requirements of your outdoor gathering. This makes gas fire pits a versatile option for outdoor heating, capable of adapting to varying needs and conditions.
Factors Impacting Warmth
While the heat output of a gas fire pit is a primary determinant of its warming capability, several other factors can influence the perceived warmth. These include:
Proximity: The closer you are to the fire pit, the more heat you'll feel. This seems intuitive, but it's essential when planning seating arrangements around a fire pit.
Wind and Weather Conditions: Wind can disperse heat, reducing the warmth you feel from a fire pit. Similarly, colder ambient temperatures will require a higher heat output from the fire pit to achieve a comfortable level of warmth.
Heat Distribution Media: As mentioned earlier, the material used within the fire pit, such as lava rocks or fire glass, can impact how the heat is absorbed and radiated.
Fire Pit Design: Some fire pits are designed with heat-retaining materials or feature designs that help to channel heat towards seating areas, increasing the warmth felt.
Size of the Outdoor Space: Larger spaces may require a fire pit with a higher heat output to achieve the same level of warmth as a smaller, more enclosed area.
Insulation: Structures around the fire pit, like walls or outdoor furniture, can help to contain and reflect heat, enhancing the perceived warmth.
Type and Quality of Fuel: The quality and type of gas used (propane or natural gas) may influence the efficiency of combustion and, therefore, the amount of heat produced.
By understanding these factors, you can take steps to optimise your outdoor setup for maximum warmth and comfort. It's not just about the power of the fire pit; it's also about how you use it and the environment in which it's placed.

The Role of Wind and Weather
Environmental conditions, particularly wind and weather, play a significant role in determining the perceived warmth of a gas fire pit.
Wind: Wind is a critical factor because it can carry heat away from your seating area, reducing the effectiveness of your fire pit. A gusty day can cause the heat to disperse quickly, making the fire pit seem less warm than it actually is. Wind can also affect the flame stability, causing flickering or even extinguishing the flames in severe cases. To mitigate the wind's effect, consider strategic positioning of the fire pit or using a wind guard - a glass or metal barrier designed to shield the flames from the wind.
Temperature: The ambient temperature also impacts the warmth you feel from a gas fire pit. The fire pit must work harder on colder days or nights to provide the same comfort level. You might need to turn up the gas and create a bigger flame to achieve a desirable temperature, which consumes more fuel.
Humidity: Although less significant than wind or temperature, humidity can influence how quickly heat dissipates. Dry air tends to allow heat to radiate more effectively than humid air.
Rain or Snow: Precipitation can affect a fire pit's operation. While many fire pits are designed to withstand such conditions, rain or snow can cool the surrounding air and the fire pit, reducing the heat you feel. It's also essential to ensure your fire pit is properly covered when not in use to prevent water from getting into the gas lines, which could cause operational issues.
Understanding how wind and weather can impact the heat from your gas fire pit is crucial for enjoying it to the fullest. Considering these elements, you can plan and adapt accordingly through strategic placement, additional wind protection, or adjusting your expectations according to the weather forecast.
Personal Preferences and Expectations
The perception of warmth from a gas fire pit isn't just about objective measurements like BTUs or kW. Personal preferences and expectations also significantly influence how warm you feel.
Some people naturally feel colder than others due to differences in metabolism, body size, and other physiological factors. Age and health conditions can also affect how warm or cold someone feels.
In addition, clothing can make a big difference. Someone dressed warmly is likely to feel comfortable at lower temperatures than someone wearing light clothing.
Expectations can also shape perceptions of warmth. If you're used to indoor heating, you might find an outdoor fire pit doesn't feel as warm, especially on a chilly night. If you expect the heat from a gas fire pit to mimic that of a wood-burning fire, you might be disappointed, as these two types of fires produce heat differently.
Subjective Experiences Vary
Even with the same fire pit and environmental conditions, different individuals can have varied experiences. Perception of temperature is a subjective sensation that can vary greatly among individuals.
Factors like circulation and your state of mind can impact how warm or cold you feel. Furthermore, if you've been active and are generating a lot of body heat, you might feel warmer sitting by the fire pit than someone who's been sitting still.
Thus, while a gas fire pit can provide a good amount of warmth, it's important to note that experiences can vary. It's a good idea to provide options for your guests, like blankets, to ensure everyone can achieve a comfortable level of warmth regardless of their individual temperature preferences.
Comparison to Traditional Wood-Burning Fires
Gas fire pits and traditional wood-burning fires have unique characteristics that influence their warmth and overall experience.
Gas fire pits offer adjustable, consistent heat, easy operation, and smoke-free warmth, which is highly appealing for those seeking convenience and control. However, they may not reach the same heat intensity as a wood fire.
Wood-burning fires can provide intense heat and create a distinct atmosphere with crackling sounds and woodsy aromas. Yet, they require more effort to start and maintain and can produce inconsistent heat.
Consider reading our previous post, Gas vs. Wood-Burning Fire Pits: This article offers a more in-depth look at the pros and cons of each type of fire pit.
Conclusion: Do Gas Fire Pits Keep You Warm?
Yes, without a doubt, they are an excellent source of heat, but conditions matter.
Gas fire pits certainly have the potential to provide a significant amount of warmth and create a wonderful environment for your outdoor space.
However, the warmth you perceive from a gas fire pit depends on several factors. These include the pit's design and heat distribution medium, your proximity to the pit, and external conditions like wind and weather.
Beyond these, personal preferences and expectations also play a major role. Perception of warmth varies from person to person based on individual metabolism, clothing, and preconceived expectations.
While a gas fire pit may not replicate the intense heat of a large, wood-burning fire, it offers a cleaner, more controlled, and consistent source of warmth that many find preferable.
Understanding these factors can help you optimise your gas fire pit use and create a warm, welcoming environment that caters to everyone's comfort.
Subscribe to our email
Just enter your email address below to receive a monthly email with links to all the latest blog posts. Simple unsubscribe at any time.